Apr 05, 2005 In shorthanded Hold'em, the starting hands have a different value than they do in full-ring games. The small pairs, hands such as A-x, and big connectors like KJ and QT, increase in value, and small suited connectors such as 76s and 87s, decrease in value.
The key difference between full ring and shorthanded cash games involves the number of poker players. Full ring is essentially a standard poker game where nine or ten players are seated. While some poker rooms offer a maximum of five seats in their shorthanded cash games, most are usually limited to a maximum of six seats, which is why they are commonly referred to as “6-max” tables.
The 6-max cash games are hugely popular online. Some poker players prefer these shorthanded cash games simply because they like to play against fewer opponents and they get to see more hands. Others prefer the standard full ring cash games, perhaps because they’re more like the cash games that are found in live poker venues.
Strategic Considerations
Even though the only difference between the two formats is the variation in table size, they play very differently.
Starting Hand Selection
Full ring cash games allows a player to play tight by being conservative with their moves and holding out and only committing when a very strong hand comes their way. Since the blinds are paid more frequently and there are fewer players in shorthanded games, starting hand values go up significantly. When you play 6-max cash games you need to play more poker hands and play them more aggressively. Anything that is playable in mid-position in a full ring game is generally playable in any position in 6-max games. You’ll also find that you can be the first raiser much more often when in late position, simply because there are fewer players.
Aggression Adjustment
Without a doubt, one of the most important separations between a full ring and a shorthanded game is the level of aggression. If you’re making the switch from full ring to 6-max cash games then you already know that you need to open up your range of starting hands. Aggressive play is always important in poker, but even more so in shorthanded games because you must maximize your ability to play and win with marginal and lighter holdings. This does not immediately relegate the more traditional full ring conservative players, but overly tight play will certainly can count against you. In the same vein, shorthanded games can sometimes tempt players to loosen up too much and play too many weak hands, which can lead to their downfall.
Positional Considerations
Position is important in all forms of poker as it is obvious that it is more desirable to act last rather than first. Playing a hand from early position In a full ring cash game is a much bigger disadvantage than in shorthanded games, since there are more opponents who can enter the pot after you’ve acted. However this doesn’t mean your table position should be disregarded when playing 6-max. Players are more likely to miss the flop in shorthanded games which makes position very valuable post-flop. If you’re out of position then you’re opponents will have more opportunities to exploit you by stealing pots when you miss the flop.
Increased Opportunities
6-max cash games are more profitable for skilled poker players. If you’re fortunate enough to be seated with an inferior opponent then you’ll be involved in many more pots with them. This means you can exploit your edge over these weak player far more than you ever could in a full ring game, simply because there are fewer competing players. The skilled poker player also benefits from playing 6-max games because of the wider range of hands that are played, and the knowledge of how to play these hands against weaker opponents, who might be clueless.
Bluffing and Value Betting
Although there are increased opportunities in shorthanded games and it is generally easier to bluff, you need to temper this with the realization that your fellow poker players know that aggressive play is the order of the day and you’ll get called much more frequently. That is the bad news – the good news is that due to the prevalent mind set in shorthanded games your value bets have a much higher likelihood of being called.
In shorthanded games you may be able to confuse your opponents by making value bets that are larger than normal. These larger bets may seem like bluffs as they appear to be discouraging a call. The contrarian nature of poker (strong is weak and weak is strong) many times makes an opponent even more willing to call. Try betting about one and one half times the pot as a value bet and you might be surprised at how often you’ll be called.
Higher Variance
You’ll experience larger swings in shorthanded games. This is simply because players will be involved in more pots with weaker hands, and betting them more aggressively. Your style of play will influence how much variance you personally experience. If there is greater variance in shorthanded games, then it stands to reason that handling the highs and lows will require a larger than normal bankroll than full ring games.
What Should You Play?
This will depend on your style of poker and your thirst for action. If it’s action you crave then shorthanded play should be your game of choice. By nature of the fewer number of players, you will be forced to play more hands than when at a full table. The playable hand values go up significantly and since there are less players to act behind you, aggressive play is essential. You simply cannot just sit there and wait for premium cards.
If you’re starting out then it’s generally better to begin by playing full ring games. This will allow you to build a solid foundation and learn the basics of good cash game play with less risk to your bankroll and your ego. Once you’ve gained the necessary experience and skills you can then progress to the shorthanded 6-max tables and get a feel for what kind of mixture of patience and aggression that’s required to succeed.
Related Lessons
By Tim Ryerson
Tim is from London, England and has been playing poker since the late 1990’s. He is the ‘Editor-in-Chief’ at Pokerology.com and is responsible for all the content on the website.
In the poker game of Texas hold 'em, a starting hand consists of two hole cards, which belong solely to the player and remain hidden from the other players. Five community cards are also dealt into play. Betting begins before any of the community cards are exposed, and continues throughout the hand. The player's 'playing hand', which will be compared against that of each competing player, is the best 5-card poker hand available from his two hole cards and the five community cards. Unless otherwise specified, here the term hand applies to the player's two hole cards, or starting hand.
- 2Limit hand rankings
Essentials[edit]
There are 1326 distinct possible combinations of two hole cards from a standard 52-card deck in hold 'em, but since suits have no relative value in this poker variant, many of these hands are identical in value before the flop. For example, A♥J♥ and A♠J♠ are identical in value, because each is a hand consisting of an ace and a jack of the same suit.
Therefore, there are 169 non-equivalent starting hands in hold 'em, which is the sum total of : 13 pocket pairs, 13 × 12 / 2 = 78 suited hands and 78 unsuited hands (13 + 78 + 78 = 169).
These 169 hands are not equally likely. Hold 'em hands are sometimes classified as having one of three 'shapes':
- Pairs, (or 'pocket pairs'), which consist of two cards of the same rank (e.g. 9♠9♣). One hand in 17 will be a pair, each occurring with individual probability 1/221 (P(pair) = 3/51 = 1/17).
An alternative means of making this calculation
First Step As confirmed above.
There are 2652 possible combination of opening hand.
Second Step
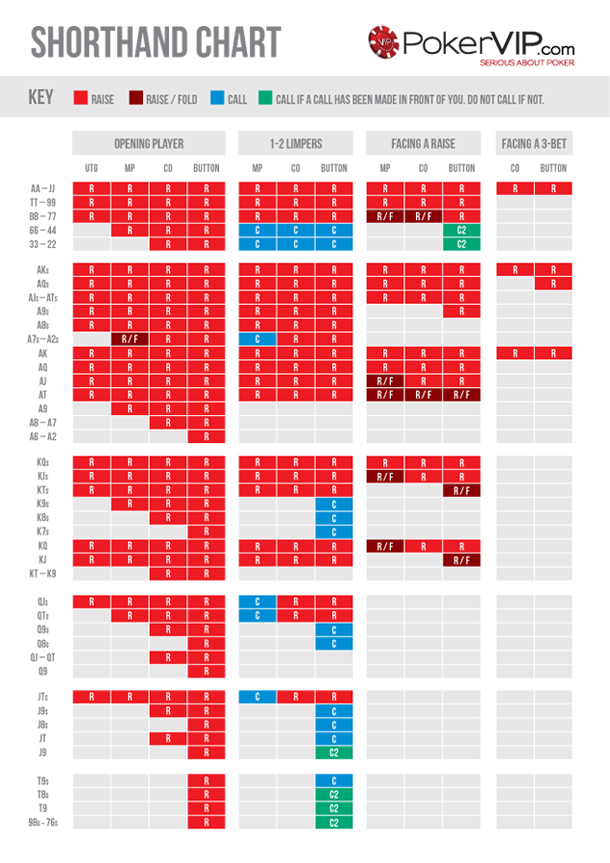
Short Handed Poker Starting Hands U R Rr
There are 6 different combos of each pair. 9h9c, 9h9s, 9h9d, 9c9s, 9c9d, 9d9s
To calculate the odds of being dealt a pair
2652 (possible opening hands) divided by 12 (the number of any particular pair being dealt. As above)
2652/12 = 221
Short Handed Poker Starting Hands Ranked
- Suited hands, which contain two cards of the same suit (e.g. A♣6♣). Four hands out of 17 will be suited, and each suited configuration occurs with probability 2/663 (P(suited) = 12/51 = 4/17).
- Offsuit hands, which contain two cards of a different suit and rank (e.g. K♠J♥). Twelve out of 17 hands will be nonpair, offsuit hands, each of which occurs with probability 2/221 (P(offsuit non-pair) = 3*(13-1)/51 = 12/17).
It is typical to abbreviate suited hands in hold 'em by affixing an 's' to the hand, as well as to abbreviate non-suited hands with an 'o' (for offsuit). That is,
- QQ represents any pair of queens,
- KQ represents any king and queen,
- AKo represents any ace and king of different suits, and
- JTs represents any jack and ten of the same suit.
Short Handed Poker Starting Hands Chart
There are 25 starting hands with a probability of winning at a 10-handed table of greater than 1/7.[1]
Limit hand rankings[edit]
Some notable theorists and players have created systems to rank the value of starting hands in limit Texas hold'em. These rankings do not apply to no limit play.
Sklansky hand groups[edit]
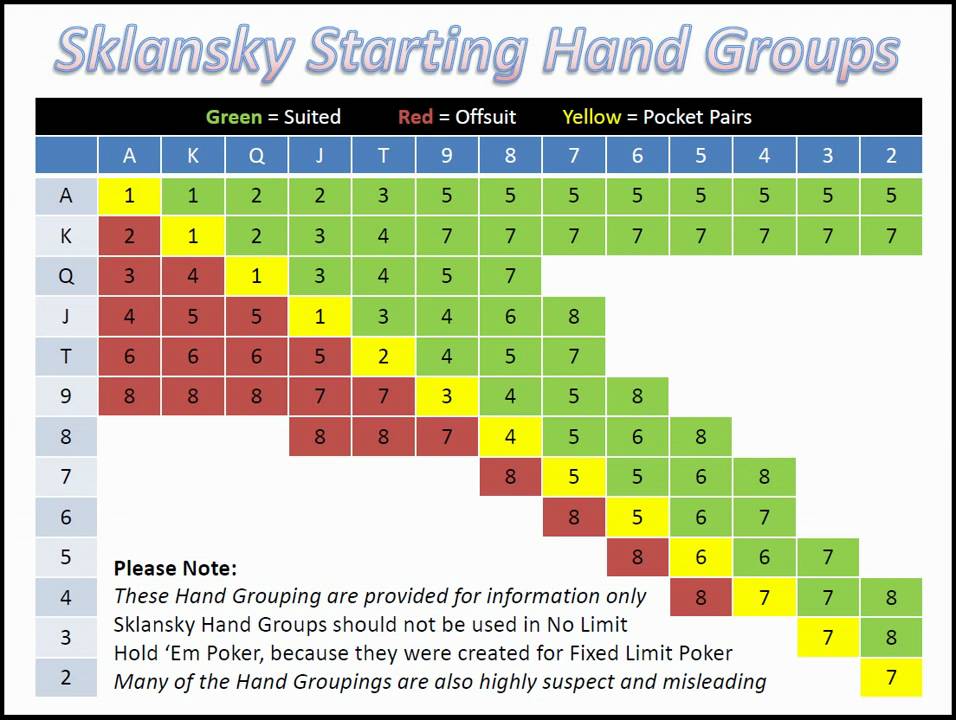
David Sklansky and Mason Malmuth[2] assigned in 1999 each hand to a group, and proposed all hands in the group could normally be played similarly. Stronger starting hands are identified by a lower number. Hands without a number are the weakest starting hands. As a general rule, books on Texas hold'em present hand strengths starting with the assumption of a nine or ten person table. The table below illustrates the concept:
Chen formula[edit]
The 'Chen Formula' is a way to compute the 'power ratings' of starting hands that was originally developed by Bill Chen.[3]
- Highest Card
- Based on the highest card, assign points as follows:
- Ace = 10 points, K = 8 points, Q = 7 points, J = 6 points.
- 10 through 2, half of face value (10 = 5 points, 9 = 4.5 points, etc.)
- Pairs
- For pairs, multiply the points by 2 (AA=20, KK=16, etc.), with a minimum of 5 points for any pair. 55 is given an extra point (i.e., 6).
- Suited
- Add 2 points for suited cards.
- Closeness
- Subtract 1 point for 1 gappers (AQ, J9)
- 2 points for 2 gappers (J8, AJ).
- 4 points for 3 gappers (J7, 73).
- 5 points for larger gappers, including A2 A3 A4
- Add an extra point if connected or 1-gap and your highest card is lower than Q (since you then can make all higher straights)
Phil Hellmuth's: 'Play Poker Like the Pros'[edit]
Phil Hellmuth's 'Play Poker Like the Pros' book published in 2003.
| Tier | Hands | Category |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AA, KK, AKs, QQ, AK | Top 12 Hands |
| 2 | JJ, TT, 99 | |
| 3 | 88, 77, AQs, AQ | |
| 4 | 66, 55, 44, 33, 22, AJs, ATs, A9s, A8s | Majority Play Hands |
| 5 | A7s, A6s, A5s, A4s, A3s, A2s, KQs, KQ | |
| 6 | QJs, JTs, T9s, 98s, 87s, 76s, 65s | Suited Connectors |
Statistics based on real online play[edit]
Statistics based on real play with their associated actual value in real bets.[4]
| Tier | Hands | Expected Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | AA, KK, QQ, JJ, AKs | 2.32 - 0.78 |
| 2 | AQs, TT, AK, AJs, KQs, 99 | 0.59 - 0.38 |
| 3 | ATs, AQ, KJs, 88, KTs, QJs | 0.32 - 0.20 |
| 4 | A9s, AJ, QTs, KQ, 77, JTs | 0.19 - 0.15 |
| 5 | A8s, K9s, AT, A5s, A7s | 0.10 - 0.08 |
| 6 | KJ, 66, T9s, A4s, Q9s | 0.08 - 0.05 |
| 7 | J9s, QJ, A6s, 55, A3s, K8s, KT | 0.04 - 0.01 |
| 8 | 98s, T8s, K7s, A2s | 0.00 |
| 9 | 87s, QT, Q8s, 44, A9, J8s, 76s, JT | (-) 0.02 - 0.03 |
Nicknames for starting hands[edit]
In poker communities, it is common for hole cards to be given nicknames. While most combinations have a nickname, stronger handed nicknames are generally more recognized, the most notable probably being the 'Big Slick' - Ace and King of the same suit, although an Ace-King of any suit combination is less occasionally referred to as an Anna Kournikova, derived from the initials AK and because it 'looks really good but rarely wins.'[5][6] Hands can be named according to their shapes (e.g., paired aces look like 'rockets', paired jacks look like 'fish hooks'); a historic event (e.g., A's and 8's - dead man's hand, representing the hand held by Wild Bill Hickok when he was fatally shot in the back by Jack McCall in 1876); many other reasons like animal names, alliteration and rhyming are also used in nicknames.
Notes[edit]
- ^No-Limit Texas Hold'em by Angel Largay
- ^David Sklansky and Mason Malmuth (1999). Hold 'em Poker for Advanced Players. Two Plus Two Publications. ISBN1-880685-22-1
- ^Hold'em Excellence: From Beginner to Winner by Lou Krieger, Chapter 5, pages 39 - 43, Second Edition
- ^http://www.pokerroom.com/poker/poker-school/ev-stats/total-stats-by-card/
- ^Aspden, Peter (2007-05-19). 'FT Weekend Magazine - Non-fiction: Stakes and chips Las Vegas and the internet have helped poker become the biggest game in town'. Financial Times. Retrieved 2010-01-10.
- ^Martain, Tim (2007-07-15). 'A little luck helps out'. Sunday Tasmanian. Retrieved 2010-01-10.
